Inter process communication (IPC) is used for exchanging data between multiple threads in one or more processes or programs. The Processes may be running on single or multiple computers connected by a network. The full form of IPC is Inter-process communication.
It is a set of programming interface which allow a programmer to coordinate activities among various program processes which can run concurrently in an operating system. This allows a specific program to handle many user requests at the same time.
Since every single user request may result in multiple processes running in the operating system, the process may require to communicate with each other. Each IPC protocol approach has its own advantage and limitation, so it is not unusual for a single program to use all of the IPC methods.
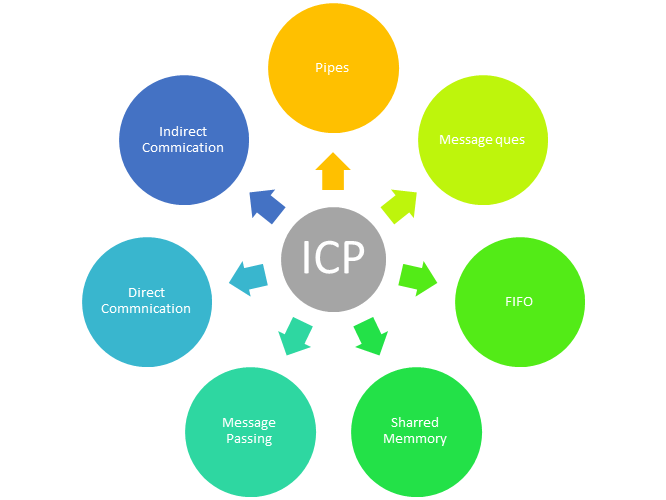
Here, are few important methods for interprocess communication:

Pipe is widely used for communication between two related processes. This is a half-duplex method, so the first process communicates with the second process. However, in order to achieve a full-duplex, another pipe is needed.
It is a mechanism for a process to communicate and synchronize. Using message passing, the process communicates with each other without resorting to shared variables.
IPC mechanism provides two operations:
A message queue is a linked list of messages stored within the kernel. It is identified by a message queue identifier. This method offers communication between single or multiple processes with full-duplex capacity.
In this type of inter-process communication process, should name each other explicitly. In this method, a link is established between one pair of communicating processes, and between each pair, only one link exists.
Indirect communication establishes like only when processes share a common mailbox each pair of processes sharing several communication links. A link can communicate with many processes. The link may be bi-directional or unidirectional.
Shared memory is a memory shared between two or more processes that are established using shared memory between all the processes. This type of memory requires to protected from each other by synchronizing access across all the processes.
Communication between two unrelated processes. It is a full-duplex method, which means that the first process can communicate with the second process, and the opposite can also happen.
Here, are the reasons for using the interprocess communication protocol for information sharing:
The following are a few important terms used in IPC:
Semaphores: A semaphore is a signaling mechanism technique. This OS method either allows or disallows access to the resource, which depends on how it is set up.
Signals: It is a method to communicate between multiple processes by way of signaling. The source process will send a signal which is recognized by number, and the destination process will handle it.
| Like FIFOS | Unlike FIFOS |
|---|---|
| It follows FIFO method | Method to pull specific urgent messages before they reach the front |
| FIFO exists independently of both sending and receiving processes. | Always ready, so don’t need to open or close. |
| Allows data transfer among unrelated processes. | Not have any synchronization problems between open & close. |
You Might Like: